
Top 11 cybersecurity frameworks in 2024
The digital threat landscape constantly evolves, with malicious actors launching more sophisticated attacks daily. Organizations must keep up with the latest cybersecurity frameworks to stay ahead of this dynamic threat environment.
Cybersecurity frameworks provide an organized approach to managing cybersecurity risks, mitigating potential vulnerabilities, and improving overall digital defense. As enterprises continue to integrate digital technologies into their operations, staying up to date with the most current cybersecurity frameworks is increasingly important.
From the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), cybersecurity frameworks are an essential part of any IT operation. Let’s look at their applications, along with 11 of the top cybersecurity frameworks in 2024.
What are cybersecurity frameworks, and why are they necessary?
A cybersecurity framework is a set of policies, practices, and procedures implemented to create an effective cybersecurity posture. These frameworks provide organizations with the guidance to protect their assets from cyberthreats by identifying, assessing, and managing risks that could lead to data breaches, system outages, or other disruptions.
Cybersecurity frameworks help organizations develop and maintain an effective cybersecurity strategy that meets the specific needs of their environment. Through evaluating current security practices and identifying gaps in protection, these frameworks help cybersecurity teams implement appropriate safeguards to protect critical assets.
If you’re interested in introducing a cybersecurity framework into your MSP operations, Building a Framework for MSP Success can help get you started.
Cybersecurity frameworks to consider
Information security is a dynamic field that encompasses a wide range of technologies, frameworks, and best practices. Appropriate cybersecurity frameworks and solutions will vary significantly across organizations depending on the industry, scale, and scope of the organization’s operations. Here are some of the most widely used cybersecurity frameworks in 2024:
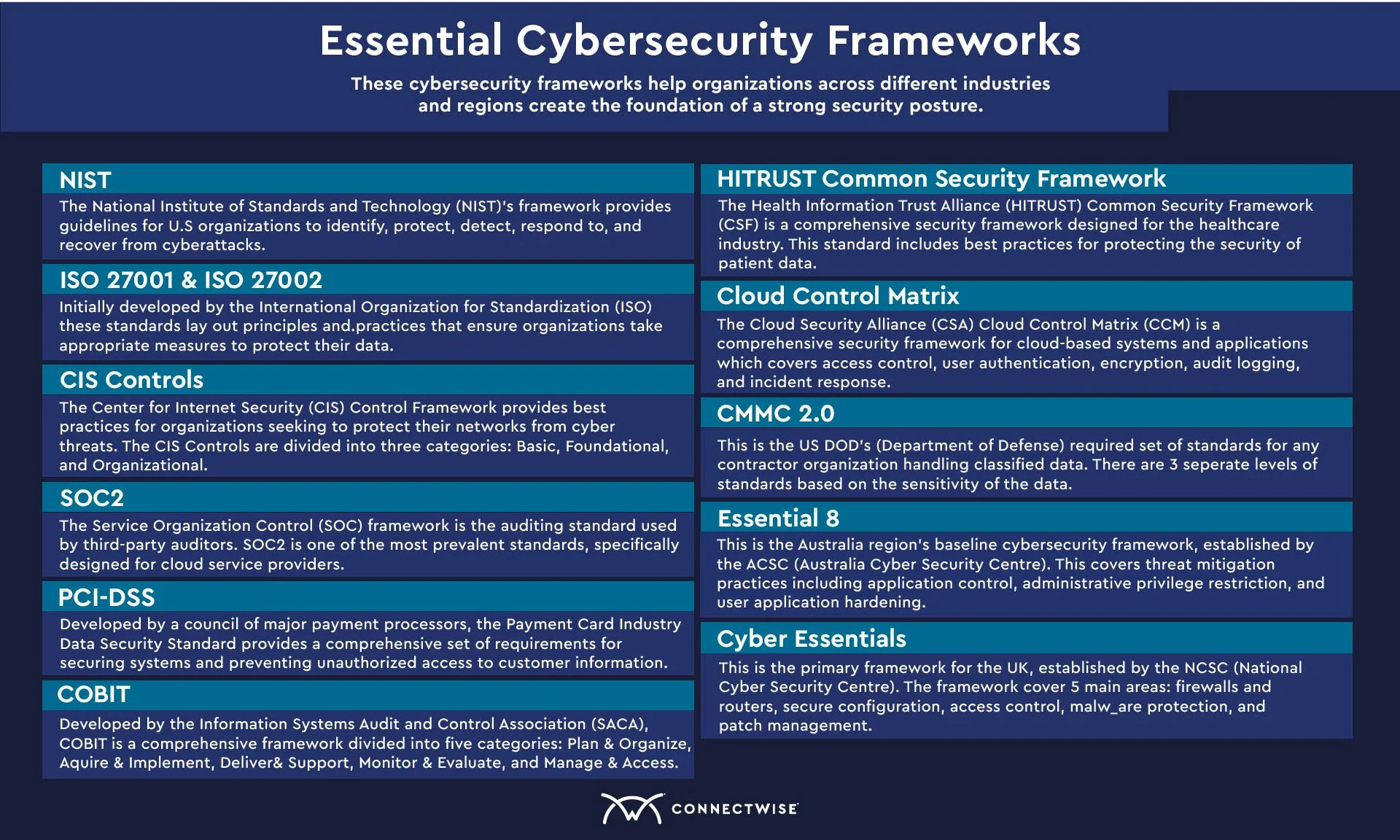
1. NIST
The NIST is a governmental agency responsible for advancing technology and security standards within the United States. NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework provides guidelines for organizations to identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cyberattacks. The framework was created in 2014 as guidance for federal agencies, but the principles apply to almost any organization seeking to build a secure digital environment.
In its second version, NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework is a comprehensive set of best practices for organizations looking to improve their cybersecurity posture. It includes detailed guidance on risk management, asset management, identity and access control, incident response planning, supply chain management, and more.
Building on previous versions, NIST Cybersecurity Framework version 2.0 was published in February 2024, and it contains new features that highlight the importance of governance and supply chains. Acknowledging the importance of cybersecurity for small businesses, NIST also published resources specifically tailored to small and midsized businesses (SMBs) with modest or no cybersecurity plans currently in place. MSPs can leverage these tools to assist clients in strengthening their cybersecurity posture.
2. ISO 27001 and ISO 27002
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 are two of the most common standards for information security management today. These standards provide a comprehensive framework for organizations looking to protect their data through robust policies and best practices.
Initially developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), these standards lay out principles and practices that ensure organizations take appropriate measures to protect their data. From asset management and access control to incident response and business continuity, these standards provide detailed guidelines to help organizations secure their networks.
ISO 27001 is an international standard that provides a systematic approach to risk assessment, control selection, and implementation. It includes requirements for establishing an information security management system (ISMS).
ISO 27002 is a code of practice that outlines more specific and detailed cybersecurity controls. When implemented together, these two standards provide organizations with a comprehensive approach to information security management.
3. CIS Controls
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Control Framework provides best practices for organizations seeking to protect their networks from cyberthreats. This framework includes 20 controls, covering many areas of cybersecurity, including access control, asset management, and incident response.
The CIS Controls are divided into three categories: Basic, Foundational, and Organizational.
- Basic Controls focus on the essential cybersecurity measures that all organizations should implement, such as regular patching and antivirus protection.
- Foundational Controls are more advanced measures that should be taken in addition to fundamental cybersecurity protocols, such as incorporating two-factor authentication and regularly monitoring log files for suspicious activity.
- Organizational Controls are designed to provide additional protections specific to the needs of an organization’s environment, such as user awareness and training.
4. SOC2
The Service Organization Control (SOC) framework is an auditing standard used by third-party auditors to assess the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of a company’s systems and services. SOC2 is one of the most prevalent standards in this framework, specifically designed for cloud service providers.
The SOC standard requires organizations to provide detailed documentation on their internal processes and procedures related to cybersecurity, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. SOC-compliant documents must include policies such as access control measures, data encryption protocols, incident response plans, and more.
Organizations must also provide evidence of the effectiveness of their controls, such as audit logs or penetration test results, helping to ensure that their cybersecurity measures are functioning correctly and can protect their data from cyberthreats.
5. PCI-DSS
A council of major payment processors developed the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) to protect customers’ payment card data. This standard provides a comprehensive set of requirements designed to help organizations secure their systems and prevent unauthorized access to customer information.
The PCI-DSS framework includes 12 requirements organizations must meet to protect customer data. These requirements cover access control, network security, and data storage specific to the payment processing industry. It also includes measures for safeguarding customer payment card data, including encryption and tokenization technologies.
On March 31, 2024, PCI-DSS version 3.2.1 officially retired, and version 4.0 became mandatory, now requiring the use of multi-factor authentication.
6. COBIT
Developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (COBIT) is a comprehensive framework designed to help organizations manage their IT resources more effectively. This framework offers best practices for governance, risk management, and cybersecurity.
The COBIT framework is divided into five categories: Plan & Organize, Acquire & Implement, Deliver & Support, Monitor & Evaluate, and Manage & Assess. Each category contains specific processes and activities to help organizations manage their IT resources effectively.
COBIT also includes detailed data security and protection guidelines, covering access control, user authentication, encryption, audit logging, and incident response areas. These guidelines provide organizations with a comprehensive set of measures that can be used to protect their systems from cyberthreats.
7. HITRUST Common Security Framework
The Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST) Common Security Framework (CSF) is a comprehensive cybersecurity framework designed for the healthcare industry. This standard includes best practices for protecting the security of patient data, covering areas such as access control, identity and access management, encryption, audit logging, and incident response.
The HITRUST CSF includes detailed cybersecurity governance, risk management, and compliance requirements, helping organizations meet relevant regulatory requirements while protecting their systems from potential cyberthreats.
8. Cloud Control Matrix
The Cloud Security Alliance’s (CSA) Cloud Control Matrix (CCM) is a comprehensive cybersecurity framework for cloud-based systems and applications which covers access control, user authentication, encryption, audit logging, and incident response.
Like HITRUST, the CCM includes detailed guidelines for cybersecurity governance and risk management aimed at helping organizations meet relevant regulatory standards.
9. CMMC 2.0
CMMC 2.0 (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification) is the latest version of the US Department of Defense’s (DoD) framework, announced in 2021. This was designed to protect national cybersecurity information by creating a set of consistent cybersecurity standards for any organization working with the DoD.
Some of the major changes from 1.0 to 2.0 include:
- Allowing self-assessment for some requirements to help ease compliance
- Creating priorities to protect DoD information
- Building better cooperation between organizations and the DoD as cyberthreats evolve
Within CMMC 2.0., there are three separate levels based on the sensitivity of data an organization processes. Each level has an increased number of required practices as well as the intensity of assessments. At the baseline level 1, there are 17 practices in place with an annual self-assessment. At level 3, over 110 practices are required, along with triennial government-led assessments.
Country-specific cybersecurity frameworks
Along with the list above, there are several more cybersecurity frameworks that are specifically designed for the compliance needs of certain countries and regions. While these may not apply to every MSP, it’s still a good idea to have a basic awareness and understanding of them. Here are some key examples below:
10. Essential 8
The Essential 8 is Australia’s baseline cybersecurity framework that all organizations are recommended to follow, like the NIST Framework in the US. Established by the Australia Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) in 2017, this serves as a baseline set of minimum best practices to avoid compromised systems. Note that, unlike many other frameworks, it specifically focuses on Microsoft Windows-based networks.
The titular Essential 8 represents the following threat mitigation practices:
- Application control
- Patch applications
- Configuring Microsoft Office macro settings
- User application hardening
- Restricting administrative privileges
- Patching operating systems
- Multi-factor authentication
- Regular backups
The ACSC also has implemented the Essential 8 Maturity Model, which adjusts recommendations for the framework based on the capabilities of both the organization and potential threat actors.
Check out our blog series for a deep dive into the Essential Eight framework, showcasing strategies and steps for implementing these critical controls.
11. Cyber Essentials
Cyber Essentials is the UK’s primary framework, and it was established by the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) in 2014. The framework is built around five main technical controls designed to protect against the most common cyber attacks:
- Firewalls and routers
- Secure configuration
- Access control
- Malware protection
- Patch management/software updates
Along with providing a base set of standards to protect organizations, compliance with Cyber Essentials is required for some UK government contracts. There are two levels of certification available: a basic self-assessment and the Cyber Essentials Plus certification, which requires a technical check-in from a third-party.
Overall, these top cybersecurity frameworks cover various approaches to handling cybersecurity challenges. Before choosing one, it is essential to evaluate your organization’s needs and determine which framework best meets them. The proper framework should help you stay secure by providing detailed guidelines and procedures for protecting against pertinent threats to your digital assets. With that said, how do you decide what is the best fit for your business?
How to choose the proper cybersecurity framework for your MSP
When selecting a cybersecurity framework, consider both your organization’s and your clients’ specific needs. Different frameworks are designed for different environments and requirements, so researching the various frameworks and determining which is applicable is a crucial first step.
To help you decide which cybersecurity framework is the best fit, we have created the MSP+ Cybersecurity Framework & Playbooks for every stage of the cybersecurity journey. Use this guide to help define what good cybersecurity looks like, or visit the ConnectWise Cybersecurity Center for more information on keeping your customers and business safe.